Ransomware attacks can disrupt an organization’s business and be costly to resolve. They are also lucrative for criminals. This blog will:
- Define ransomware and explain how it affects organizations.
- Review the evolution of ransomware.
- Discuss recent recommendations from the federal government in the updated version of their #StopRansomware Guide.
- Share tools and tactics to help organizations protect themselves from ransomware attacks.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files or restricts access to a computer, making the files or device inaccessible to the user. The attackers then demand a ransom payment from the victim in exchange for a decryption key or tool that can restore access to the encrypted files or unlock the system.
Ransomware attacks are a favorite of cyber criminals, and it’s easy to see why. Criminals often start with a simple phishing attack where they craft an email that will trick an employee into clicking on a malicious link or visiting an infected website. From there, the attackers can encrypt files on hard drives accessible by that user or move laterally to other devices.
The damaging effects of ransomware attacks are not limited to the targeted organization. Rather, they can have far-reaching effects: the 2017 WannaCry and Petya/NotPetya attacks in the UK forced over 80 National Health Service centers to shut down. The NHS was forced to cancel almost 20,000 patient appointments, and five hospitals had to divert ambulances to other facilities. More recently, ransomware attacks on hospitals in Germany and Alabama contributed to patient deaths.
The Costs of Ransomware Attacks
A ransomware attack can shut down an organization, making it unable to run equipment, deliver services, and invoice customers. Financial and reputational damage to an organization from a ransomware attack can also be substantial. IBM Security’s Cost of a Data Breach report found the average cost of a ransomware attack —not including the cost of the ransom itself — was over $4.5 million. Interestingly, the costs, which include activities such as detection of the attack and loss of business due to system downtime, were higher for organizations that did not pay the ransom for the decryption key. Please keep in mind that the FBI recommends that organization NOT pay ransoms, as this “encourages perpetrators to target more victims.”
The Evolution of Ransomware
Ransomware has come a long way since the 1989 AIDS Trojan Ransomware was delivered disguised as a survey on infected floppy disks. The 2021 Colonial Pipeline attack was one of the first instances where ransomware affected the public at large. The attack by Darkside caused Colonial to shut down pipelines that supplied 45 percent of the East Coast’s fuel.
In recent years, ransomware attacks have evolved with the introduction of double extortion tactics and Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS). The Verizon Data Breach Investigation Report (DBIR) first reported on double extortion in its 2020 report, describing it as “ransomware families that are now capturing data before encrypting so the actors can threaten to also expose the data if the ransom is not paid.” Double extortion has increased the pressure on victims to pay, as the consequences of data exposure can be severe. RaaS models have made ransomware more accessible to a broader range of cybercriminals. RaaS has allowed less technically skilled individuals to rent or purchase ransomware kits, enabling them to launch attacks without significant technical expertise.
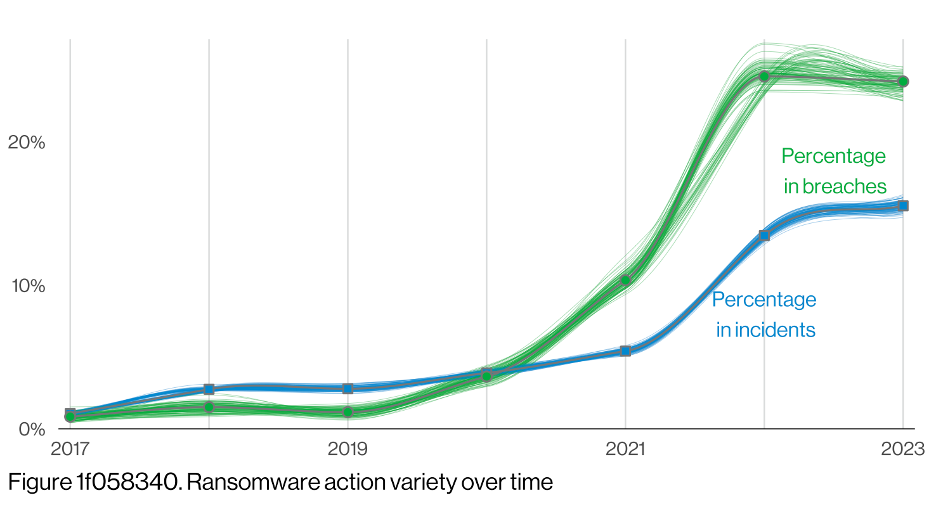
The 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigation Report found ransomware accounted for 24 percent of all breaches, up from roughly four percent in 2020.
US Government Responses to Ransomware
#StopRansomware Guide
In 2020, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and Multi-State Information Sharing & Analysis Center (MS-ISAC) published a Stop Ransomware guide to help organizations understand and protect themselves from ransomware attacks. As ransomware attacks continued, the federal government recognized the need for additional action.
In 2022, Congress passed the Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act of 2022 (CIRCIA). While the focus of CIRCIA is information sharing, it also ordered the creation of the Joint Ransomware Task Force (JRTF). The JRTF, co-chaired by CISA and the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), coordinates existing interagency efforts “to coordinate an ongoing nationwide campaign against ransomware attacks, and identify and pursue opportunities for international cooperation.”
In May 2023, the JRTF published an updated #StopRansomware Guide. The guide includes two primary resources for organizations: Ransomware and Data Extortion Prevention Best Practices, and a Ransomware and Data Extortion Response Checklist
What’s New in the #StopRansomware Guide
In addition to adding the FBI and NSA as co-authors and incorporating the #StopRansomware hashtag, Version 2.0 includes four significant additions:
- Recommendations for preventing common initial infection vectors: Good defensive measures can block an attack before criminals gain a foothold. The guide specifically covers several attack vectors, including internet-facing vulnerabilities and misconfigurations, compromised credentials, phishing, precursor malware infections, and social engineering.
- Updated recommendations to address cloud backups and zero trust architecture (ZTA): Offline, encrypted cloud backups can simplify responses to ransomware attacks. ZTA “assumes breach” and requires granular access control policies, making an attacker’s job more difficult.
- Expanded the ransomware response checklist with threat hunting tips for detection and analysis: Threat hunting is a proactive cybersecurity practice that involves searching for and identifying potential threats or malicious activities within an organization’s network or systems. This could include newly created accounts with elevated privileges, anomalous VPN device logins, and unexpected PowerShell execution.
- Mapped recommendations to CISA’s Cross-Sector Cybersecurity Performance Goals (CPGs): CPGs are a minimum set of practices and protections that CISA and NIST recommend all organizations implement.
How Defendify Can Help
Defendify aims to deliver streamlined, All-In-One Cybersecurity® that provides organizations with comprehensive, ongoing protection. We provide our customers with layered security solutions that support the #StopRansomware recommendations and enable them to understand their security posture, prioritize activities to improve their security, educate their users, and defend their systems from sophisticated cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity Assessments: Stopping ransomware and other attacks requires awareness of weaknesses in your defenses. Defendify offers a Cybersecurity Risk Assessment Tool that identifies deficiencies and prioritizes risk mitigation efforts. A questionnaire guides teams through the assessment and maps to standards such as ISO 27001, Center for Internet Security (CIS) Critical Security Controls, or the NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
Vulnerability Scanning: #StopRansomware recommendations include scanning for internet-facing vulnerabilities. This requires ongoing diligence, as new vulnerabilities are disclosed daily. The Defendify Vulnerability Scanner provides automated scanning to identify and prioritize vulnerabilities in your network and systems. Detailed reporting and remediation recommendations help teams understand what issues are most important to focus on first and next.
Compromised Password Scanning: Stolen credentials allow criminals to appear as legitimate users as they access your systems. If these include elevated privileges, it allows the attacker to steal information and execute ransomware attacks. Defendify’s Compromised Password Scanner searches the dark web for compromised employee passwords and credentials, allowing teams to lock out users or force password resets.
Managed Detection and Response: Hackers don’t work standard business hours. Defending your systems requires 24/7/365 attention, but few organizations have the resources to staff a Security Operations Center. Defendify’s Managed Detection and Response (MDR) is an outsourced service that actively collects and correlates data from your endpoints, mobile devices, network, perimeter, cloud, and applications. It leverages advanced technology to provide faster breach detection. Our expert cybersecurity specialists analyze security events to surface suspicious activity and help contain attacks.
Phishing Simulation Tool: According to a study by IBM, 45% of ransomware attacks used phishing or social engineering as the initial attack vector. Tricking a user into clicking on a malicious link or providing credentials is a simple task for attackers. Training your employees to identify email-based attacks is an essential preventative measure that everyone must undertake. Defendify’s Phishing Simulation Tool enables you to send carefully crafted phishing emails to your employees and observe their actions.
Policies and Training: Human errors account for 95% of cybersecurity incidents. Implementing cybersecurity policy and training activities ensures that users understand how they can help improve the organization’s cybersecurity profile – including password management, authorized application and device use, and using organizational assets appropriately.
Defendify’s Technology Acceptable Use Policy communicates to employees standards for technology and data use with configurable templates to deliver tailored cybersecurity policies. Our Cybersecurity Awareness Training creates a baseline foundation of cybersecurity knowledge, while videos, simulations, and graphics to help organizations create a cybersecurity culture and become more resistant to attacks.
Next Steps
The simplicity of ransomware attacks and the willingness of victims to pay ransoms make them attractive to criminals. Cybersecurity assessments and vulnerability scanning can help reduce your organization’s attack surface. MDR can help spot and contain attacks. Training – including phishing simulations – can help put in place a “human firewall” against attacks while improving an organization’s security profile.
Looking to improve your cybersecurity posture? Let’s talk.
Resources & insights

Continuous Monitoring: Cybersecurity 24/7, 365

Becoming Ransomware Resilient

5 Tips for Implementing a Successful Social Engineering and Phishing Training Program

Continuous Monitoring: Cybersecurity 24/7, 365

Becoming Ransomware Resilient

5 Tips for Implementing a Successful Social Engineering and Phishing Training Program
Protect and defend with multiple layers of cybersecurity
Defend your business with All-In-One Cybersecurity®.
Explore layered
security
Learn more about Defendify’s three key layers and All-In-One Cybersecurity®.
How can we help?
Schedule time to talk to a cybersecurity expert to discuss your needs.
See how it works
See how Defendify’s platform, modules, and expertise work to improve security posture.








